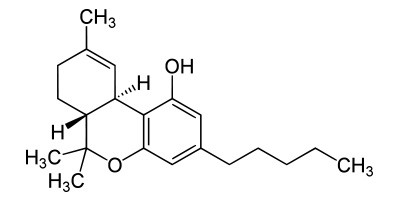
Name: THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol)
Boiling Point : 157°C
Description:
Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is a phytocannabinoid, and typically the most abundant cannabinoid present in cannabis products on the market today. THC can be derived from THCA by non-enzymatic decarboxylation during storage and consumption. It is responsible for the well-documented psychoactive effects experienced when consuming cannabis. When you smoke or ingest cannabis, THC travels into the bloodstream and eventually binds to cannabinoid receptors throughout your body. These receptor sites affect memory, concentration, pleasure, coordination, sensory and time perception, appetite and many more important functions. Mild side effects of larger doses of THC can include anxiety, elation, burning eyes, dry mouth, shaking/trembling, increased heart rate and/or shortness of breath (or at least the perception of such) and short-term memory loss. Smoking or ingesting too much THC in a short period of time can intensify and alter its effects. (via medicaljane.com)
Reported Effects:
- Psychoactive
- Sedation
- Pain Relief
- Improved Appetite
Studies:
- Ultralow doses of cannabinoid drugs protect the mouse brain from inflammation-induced cognitive damage.
- Preliminary, open-label, pilot study of add-on oral Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol in chronic post-traumatic stress disorder.
- Effect of marijuana use on outcomes in traumatic brain injury.
- Cannabis use amongst patients with inflammatory bowel disease.
- Cannabinoids for treatment of spasticity and other symptoms related to multiple sclerosis (CAMS study): multicentre randomised placebo-controlled trial.
- Δ⁹-Tetrahydrocannabinol attenuates allogeneic host-versus-graft response and delays skin graft rejection through activation of cannabinoid receptor 1 and induction of myeloid-derived suppressor cells.